USER
Seperti yang telahkitaketahui, Linux termasuksistem multiuser dimanasuatu resource bisadigunakanolehbanyak user. Setiap user biasanyadiberiruangan yang disimpanrapidalamdirektori /home. Setiap user, pada home masing-masingmemilikihakmengakses, membacaataumenulis file-file di dalam home merekasendiritetapimerekabelumtentubisamelakukanhal yang sama di home milik user lain ataudirektorimilik root. Masing-masing user bisadiberihak-hakkhusus yang berlainanuntukmengakses, membacaataumenuliskesebuah file ataudirektorioleh root. Olehkarenaitukitabisasajameninggalkan root sepanjangharidengancaramembuat home sendiri, login sebagai user biasasertamemberikanhakaksesseperlunyasaja agar tidakmembahayakansistembilasuatusaatkitamelakukankesalahan.
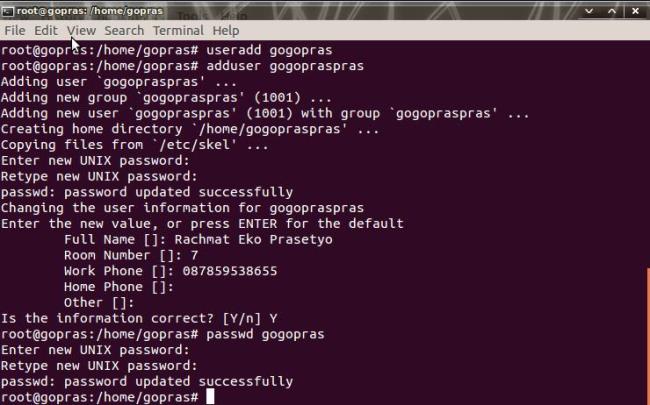
Untukmenambahkan user di linuxdapatdilakukandenganperintah adduser atauuseradd. Tetapiterdapatperbedaanpadakeduaperintahtersebut, yaitu:
adduser :
1. Menciptakan user denganmelakukan setting password.
2. Menciptakan user beserta home direktorinya.
3. Menciptakan user denganmemberikanketeranganlengkap user tersebut.
useradd :
1. Menciptakan user tanpamelakukan setting password.
2. Menciptakan user tanpaada home direktorinya.
3. Menciptakan user tanpamemberikanketeranganlengkap user tersebut.
Contoh :
- Adduser dan useradd
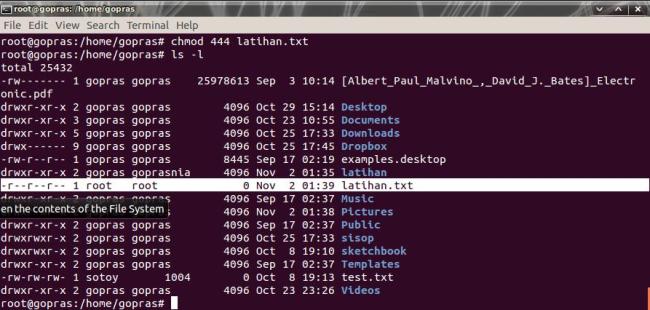
Anda jugadapatmengubah password user denganmengetikkanperintah passwd [nama user] danbisajugamenghapus user yang tidakdiinginkandenganmengetikkanperintahuserdel [nama user]. Keduaperintahtersebutdapat di eksekusi di terminal.
GROUP
Setiap user dapatbergabungkesebuah group. Group bisaberisikumpulan user lain atau program yang mempunyaikesamaantugas. Group memungkinkansebuah file bisadipergunakansecarabersamahanyaoleh user-user yang tergabungdidalam group tersebut. Olehkarenaitucaramengelompokkan user-user dalam group iniadalahsalahsatucara yang mudahbagi root untukmemberikanhakakses file-file miliknyakepadasekelompok user.
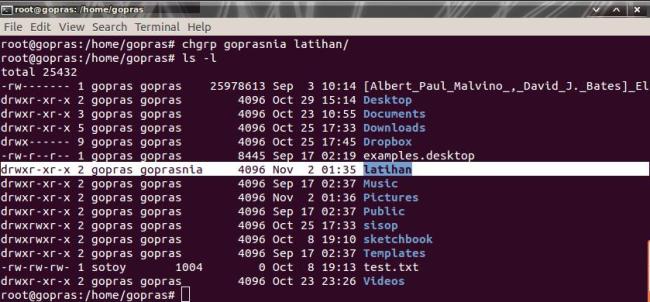
Untukmembuatsebuah group baru, Andabisamenggunakanperintah groupadd. Misalnya, Andainginmembuat group barudengannama goprasnia makaperintah yang harusdiketik di terminal adalah groupaddgoprasnia. Anda jugadapatmengubah password group denganmengetikkanperintah gpasswd [nama group] danbisajugamenghapus group yang tidakdiinginkandenganmengetikkanperintah groupdel [nama group]. Keduaperintahtersebutdapat di eksekusi di terminal.
Berikutnyaadalahmenambahkan user yang akanbergabungkedalam group goprasniaini. Informasi group disimpandalam file /etc/group, bukalahdenganmenggunakan editor kesayanganAnda. Kemudiantambahkannama-nama user yang akanbergabungdalam group
Setiapbarisdalam file /etc/group terdiridariempatsegmen yang dipisahkanolehtandatitikdua (:)
nama group : password : group id (gid) : user
Carilahbaris group goprasnia dancukuptambahkannama user yang akanbergabungdengan group goprasnia ini di segmenterakhir. Pisahkannama user dengantandakoma (,) bila user yang bergabunglebihdarisatu
Password biasanyakosongatau * ataubiarkansajabilaAndatidakmembuat password untuk group ini. Setelah file /etc/group ini di simpanmakatugasberikutnyaadalahmerubah permission dan ownership file-file yang bisadiaksesoleh group goprasnia.
PERMISSION
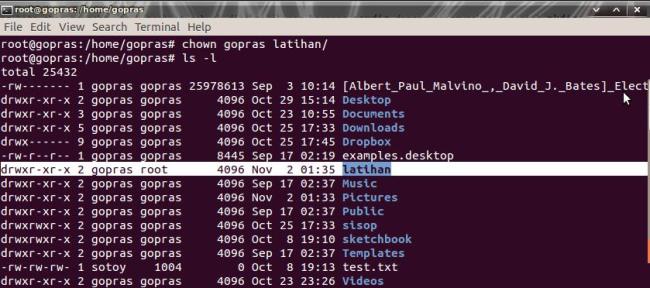
- Chown
Merubah user ID (owner) sebuah file ataudirektori.
Contohperintah :
chown [nama user] [file yang akan di edit kepemilikannya]
- Chmod
Digunakanuntukmenambahdanmengurangiijinpemakaiuntukmengaksessebuah file ataudirektori. Andadapatmenggunakansistem numeric coding atausistem letter coding. Ada tigajenis permission yang dapatdirubahyaitu r (read), w (write) dan x (execute).
Denganmenggunakan letter coding, Andadapatmerubah permission diatasuntukmasing-masing u (user), g (group), o (other) dan a (all) denganhanyamemberitanda plus (+) untukmenambahijindantanda minus (-) untukmencabutijin.